Journal list menu
Export Citations
Issue Information
Review
Safety of sodium–glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors in Asian type 2 diabetes populations
- Pages: 167-182
- First Published: 19 October 2022

Sodium glucose co-transporter-2 (SGLT-2) inhibitor have gained a central role in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus particularly owing to its cardiorenal benefits. It is generally well-tolerated and have a well-defined safety profile. This review is the first to provide a comprehensive coverage on the side effects of SGLT2i as well as their management and counseling aspects for Asian type 2 diabetes mellitus population.
Commentaries
Pancreatic islet transplantation in type 1 diabetes: Current state and future perspectives
- Pages: 183-185
- First Published: 09 November 2022
Current understanding of imeglimin action on pancreatic β-cells: Involvement of mitochondria and endoplasmic reticulum homeostasis
- Pages: 186-188
- First Published: 01 December 2022
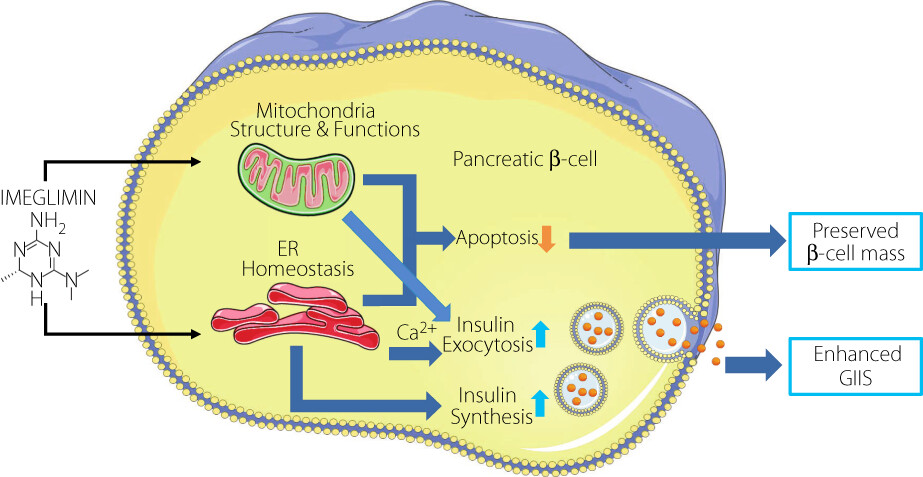
Recent preclinical studies have provided insight on imeglimin's action on pancreatic β-cells and the mechanisms underlying its clinical benefits. Imeglimin may enhance glucose-induced insulin secretion (GIIS) and inhibit apoptosis of pancreatic ß-cells leading to preserved β-cell mass by maintaining or restoring the functional and structural integrity of the mitochondria and the endoplasmic reticulum homeostasis in pancreatic β-cells.
Update
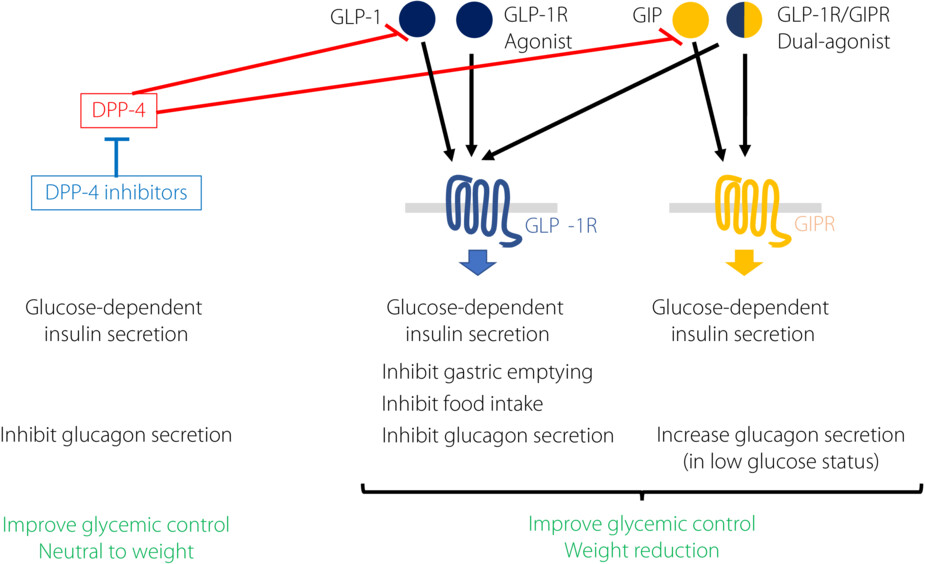
Updates of incretin-related drugs for the treatment of type 2 diabetes
- Pages: 189-192
- First Published: 14 November 2022
Articles
Basic Science and Research
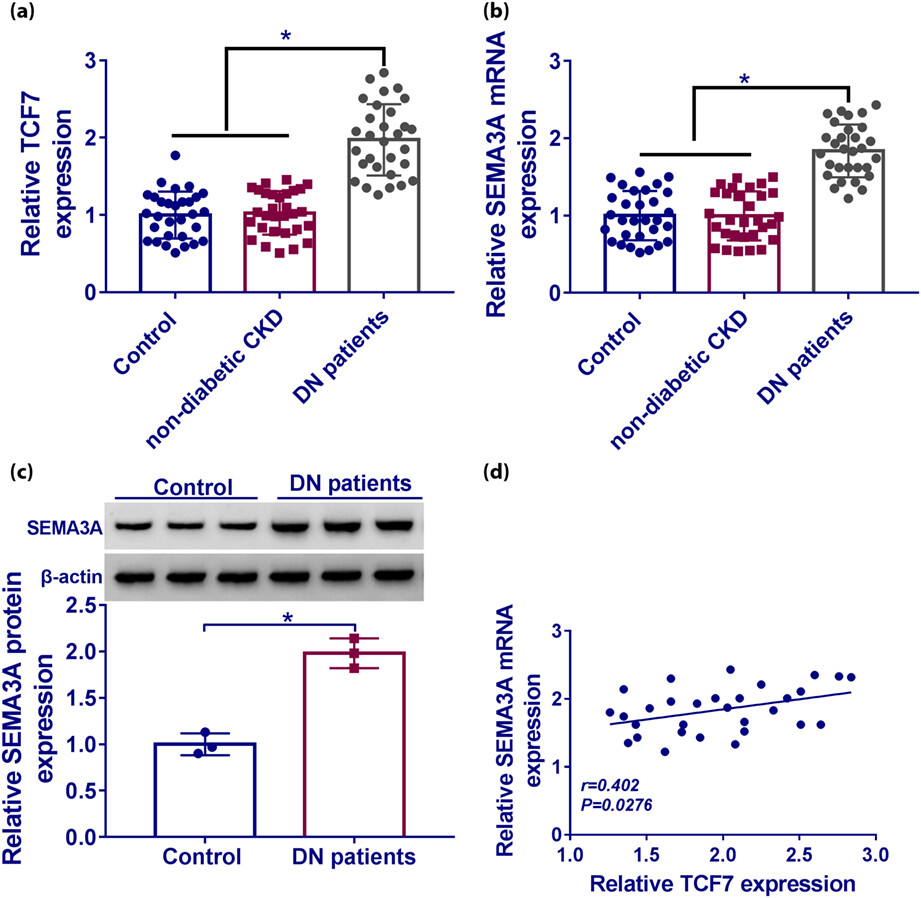
LncRNA TCF7 contributes to high glucose-induced damage in human podocytes by up-regulating SEMA3A via sponging miR-16-5p
- Pages: 193-204
- First Published: 29 December 2022
Suramin prevents the development of diabetic kidney disease by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome activation in KK-Ay mice
- Pages: 205-220
- First Published: 29 October 2022
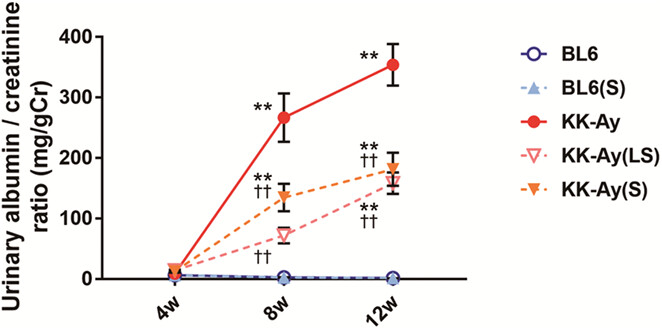
Suramin, a nonselective antagonist of the P2 receptors, suppresses NLRP3 inflammasome activation and exerts renoprotective effects in diabetic KK-Ay mice. Suramin protects against DKD development via the inhibition of P2X receptors, and can be expected to be an important drug for the treatment of DKD.
Clinical Science and Care
Clinical signs of type 1 diabetes are associated with type 2 diabetes marker transcription factor 7-like 2 polymorphism
- Pages: 221-229
- First Published: 27 October 2022
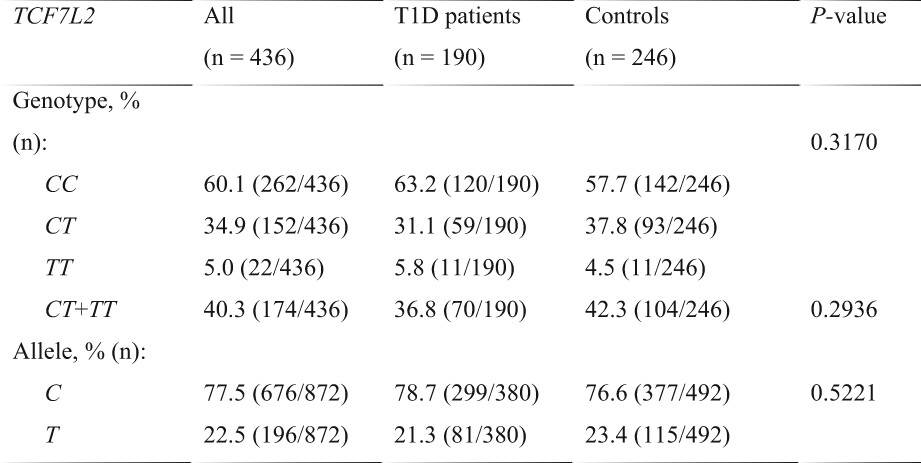
We aimed to assess possible association between TCF7L2 genotypes (rs7903146) and characteristics of type 1 diabetes including autoantibodies and C-peptide levels. Our findings about the association of TCF7L2 polymorphism with zinc transporter 8, islet antigen 2 autoantibodies and C-peptide levels in patients support the view that TCF7L2 may contribute to development of type 1 diabetes. The interaction between the TCF7L2 risk genotype and autoantibodies needs to be studied further.
Circulating selenoprotein P levels predict glucose-lowering and insulinotropic effects of metformin, but not alogliptin: A post-hoc analysis
- Pages: 230-235
- First Published: 07 December 2022
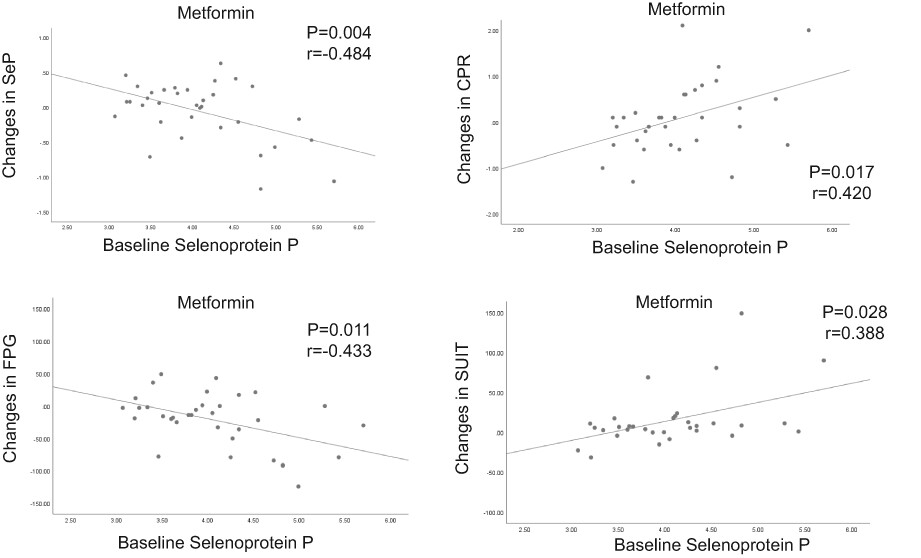
Selenoprotein P (encoded by SELENOP in humans) is a hepatokine that causes impaired insulin secretion and insulin resistance. We found that higher baseline levels of selenoprotein P significantly predicted a hypoglycemic effect and recovery of insulin secretion under metformin therapy. Selenoprotein P might be a novel biomarker for predicting the effect of metformin therapy, and could potentially be the first “tailor-made” diabetes treatment.
Characteristics of subjects with type 2 diabetes enrolled in randomized controlled trials and non-randomized controlled trials in Japan: A systematic review
- Pages: 236-246
- First Published: 21 June 2022

This study shows findings from a systematic review of RCTs and non-RCTs published in the past 10-years on adult subjects with suboptimally controlled type 2 diabetes (T2D) despite receiving one or more glucose-lowering drugs in Japan. The characteristics of studied subjects were different among study designs. Our study also found that subjects with older age and comorbidities were rarely included in both RCTs and non-RCTs.
Safety and effectiveness of dulaglutide 0.75 mg in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes in real-world clinical practice: 36 month post-marketing observational study
- Pages: 247-258
- First Published: 11 November 2022
Changes of HbA1c variability after the switch to a longer-acting insulin analog in people with type 1 diabetes
- Pages: 259-262
- First Published: 07 November 2022
Comparative efficacy of different eating patterns in the management of type 2 diabetes and prediabetes: An arm-based Bayesian network meta-analysis
- Pages: 263-288
- First Published: 13 December 2022
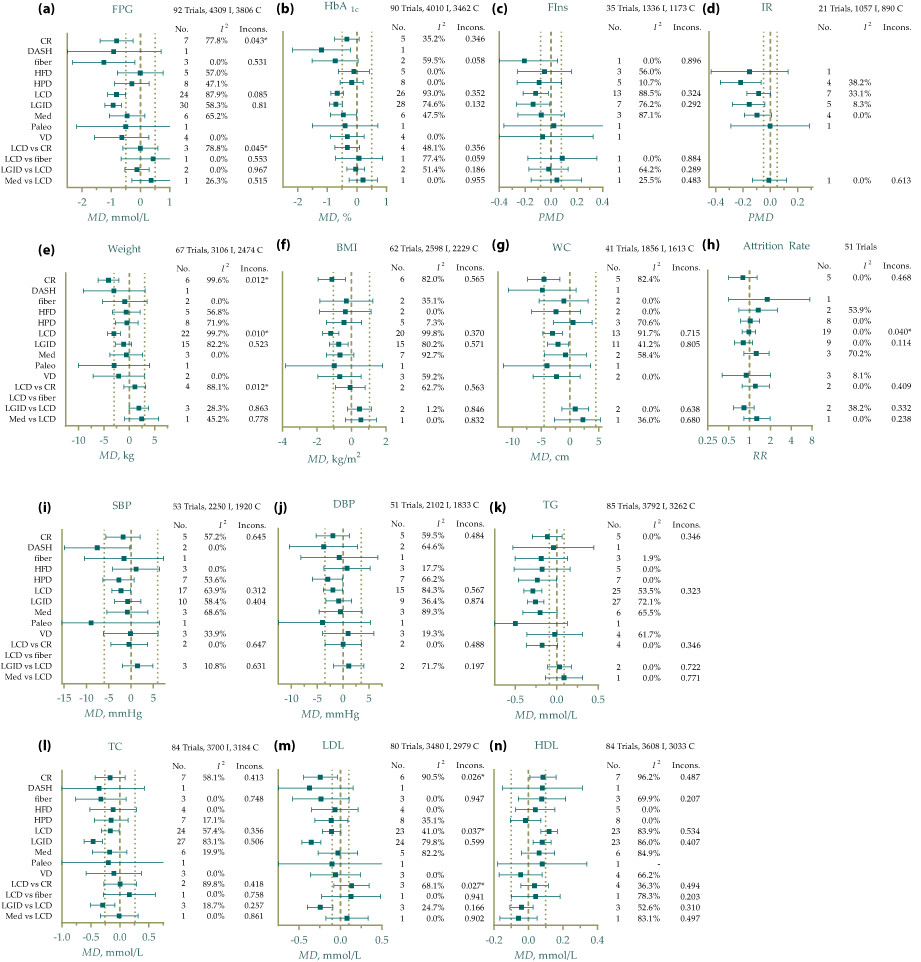
This network meta-analysis of 107 trials and nearly 9,000 participants provided conclusions on the rankings of popular dietary patterns for glycemic control, weight, blood pressure, and serum lipid profile outcomes. For each outcome, clinicians can use this work to find the most appropriate and effective diet, benefiting from this study. Heterogeneity and sensitivity should be considered, and more high-quality RCTs for new dietary patterns are needed.
Carotid atherosclerosis: An independent risk factor for small fiber nerve dysfunction in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
- Pages: 289-296
- First Published: 09 November 2022
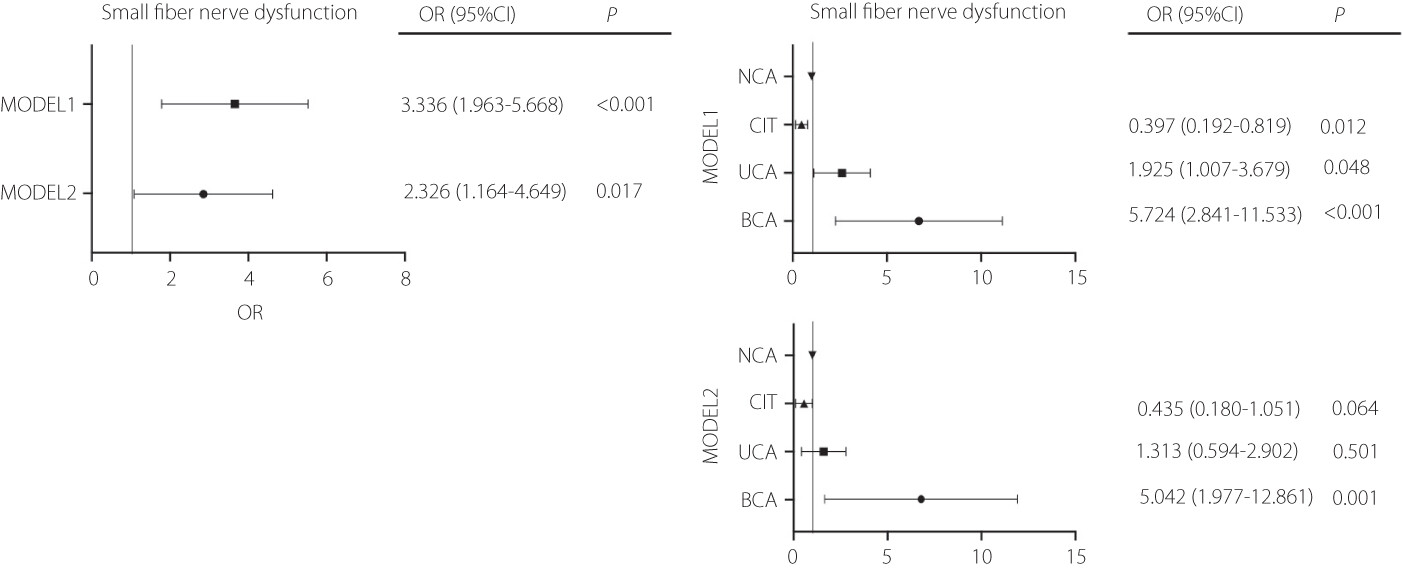
In this study, a total of 247 T2DM patients were enrolled and they all received carotid ultrasonography and quantitative sensory testing which indicates the function of small fiber nerve. And the correlation between these two parameters were analyzed by SPSS 26.0. Finally, we found that carotid atherosclerosis was significantly associated with quantitative sensory testing and found to be an independent risk factor for small fiber nerve damaging in T2DM. This study is benefit to the prevention and early diagnosis of diabetes complication especially small fiber neuropathy.
Interaction among dietary n-3 and n-6 polyunsaturated fatty acid intake, fatty acid desaturase 2 genetic variants, and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels in type 2 diabetes patients
- Pages: 297-308
- First Published: 22 November 2022
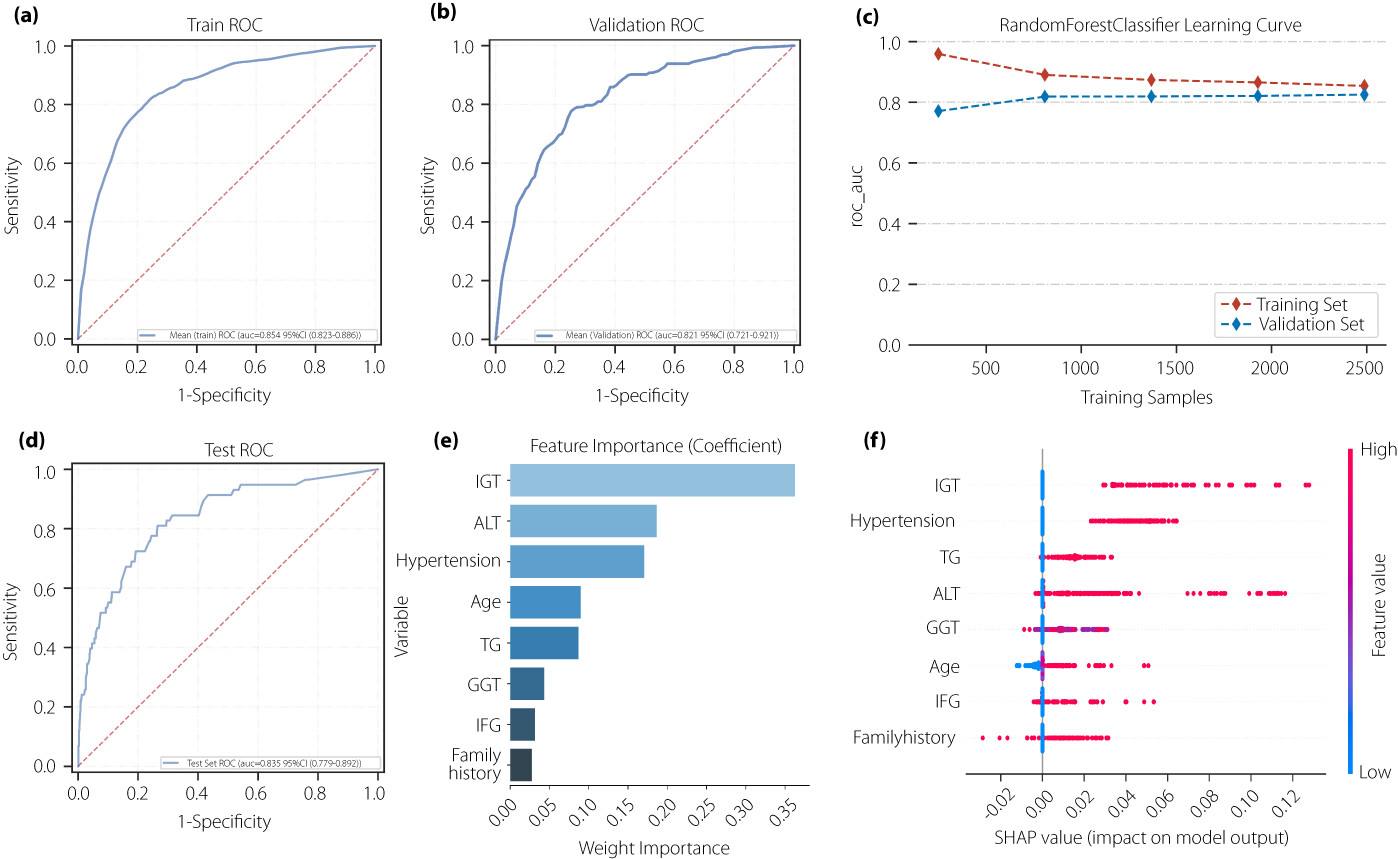
Value of machine learning algorithms for predicting diabetes risk: A subset analysis from a real-world retrospective cohort study
- Pages: 309-320
- First Published: 07 November 2022
Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the glycemic control, eating habits, and body compositions of people with diabetes mellitus: A retrospective longitudinal observational study
- Pages: 321-328
- First Published: 08 November 2022
The COVID-19 pandemic had a negative impact on the glycemic control and body composition of people with diabetes mellitus. The increased body weight and fat mass and decreased skeletal muscle mass observed during the pandemic were associated with poor glycemic control in people with diabetes mellitus.
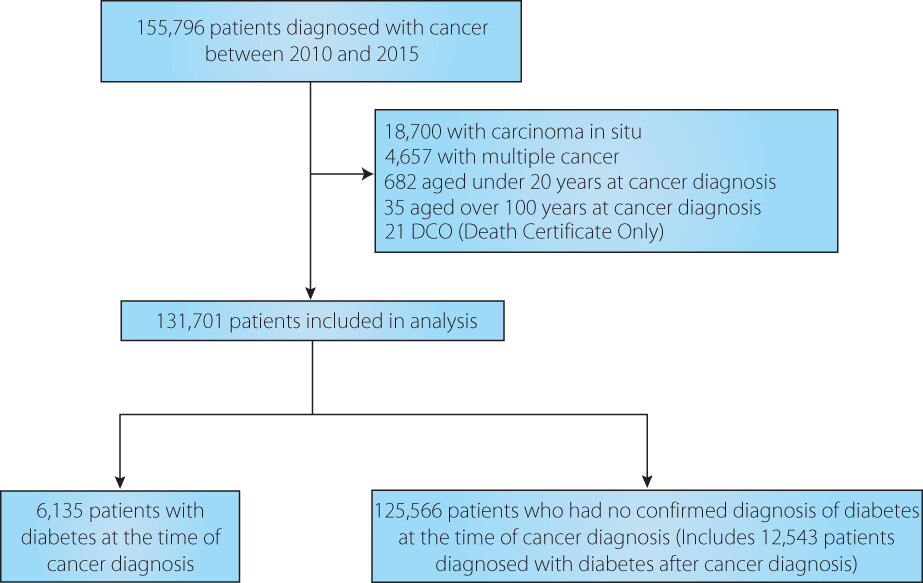
Impact of coexisting diabetes on survival and risk of developing second primary cancer in diabetes patients receiving drug therapy: A multicenter retrospective cohort study of patients with cancer in Japan
- Pages: 329-338
- First Published: 07 November 2022
Association between serum gamma glutamyl transferase and fasting blood glucose in Chinese people: A 6-year follow-up study
- Pages: 339-343
- First Published: 22 November 2022
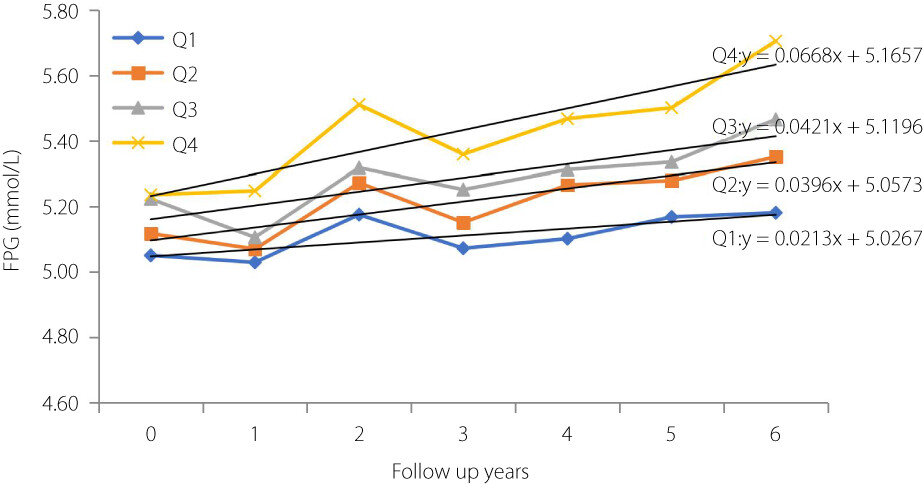
Our results showed that different baseline GGT groups were still significantly associated with increased FBG levels during follow-up. The annual mean increase in FBG levels showed a positive relationship with baseline GGT levels. This trend was even more aggregated in the highest baseline GGT group. GGT can be used for the early detection of FBG-related disorders of glucose metabolism for clinical application.
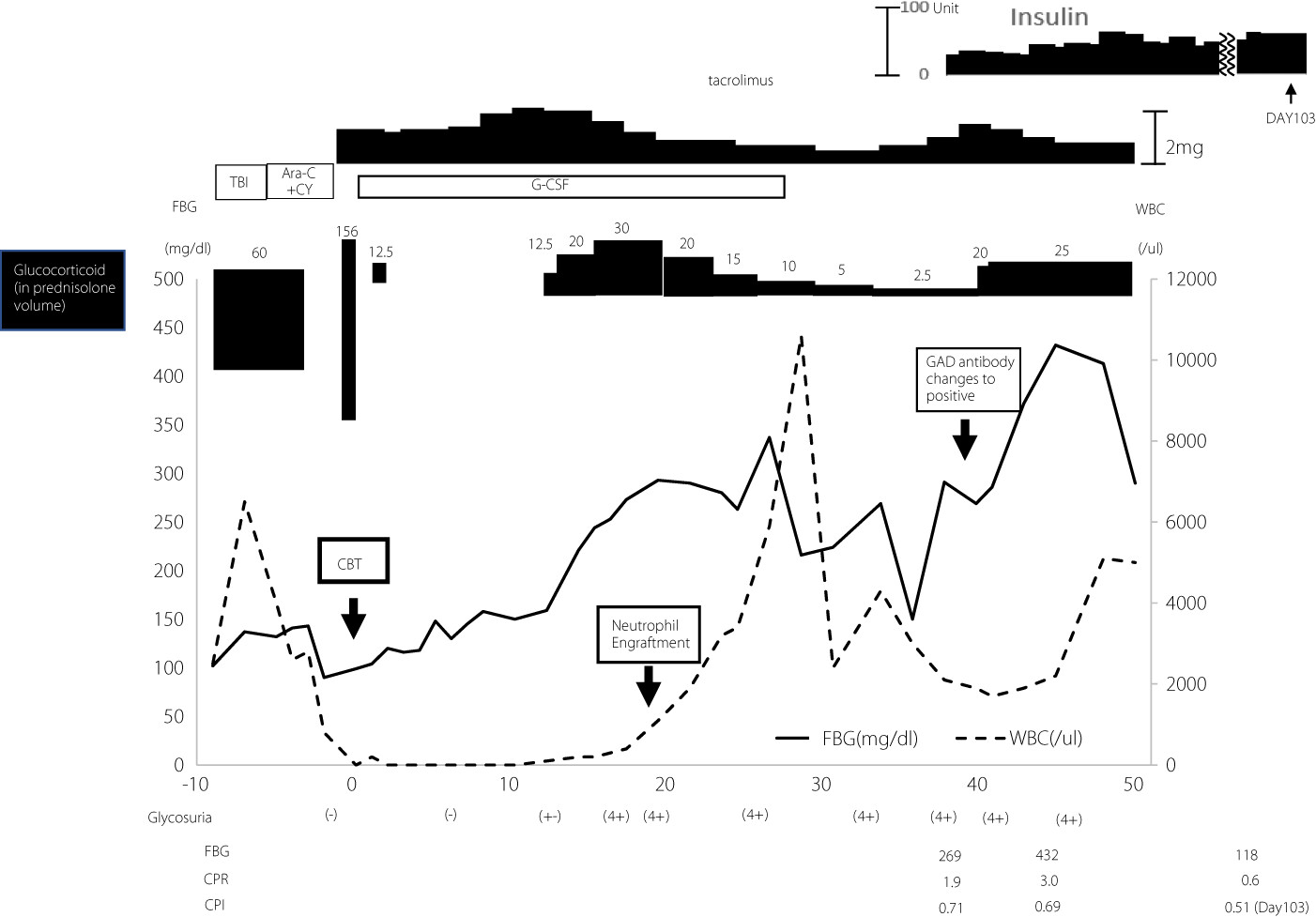
Type 1 diabetes mellitus after cord blood transplantation from an unrelated donor with a disease-sensitive haplotype
- Pages: 344-347
- First Published: 02 November 2022